| Heaviest and most valuable gold coin ever discovered |  |
 |
|
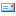
An extremely rare 200-year old gold coin was uncovered recently in the excavations of the University of Michigan and University of Minnesota at Tell Kedesh in Israel near its Lebanese border. The coin was minted in Alexandria by Ptolemy V in 191 BCE and bears the name of the wife of Ptolemy II, Arsinoë Philadephus (II). According to Dr. Donald T. Ariel, head of the Coin Department of the Israel Antiquities Authority, “This is an amazing numismatic find. The coin is beautiful and in excellent preservation. It is the heaviest gold coin with the highest contemporary value of any coin ever found in an excavation in Israel.” The coin weighs almost one ounce (27.71 grams), while most ancient gold coins weighed 4.5 grams. This extraordinary coin was apparently The obverse (‘head’) of the coin depicts Arsinoë II Philadelphus. The reverse (‘tail’) depicts two overlapping cornucopias (horns-of-plenty) decorated with fillets. The meaning of the word Philadelphus is brotherly love. Arsinoë II, daughter of Ptolemy I Soter, was married at age 15 to one of Alexander the Great’s generals, Lysimachus, king of Thrace. After Lysimachus’ death she married her brother, Ptolemy II, who established a cult in her honour. This mnaieion from Tel Kedesh attests to the staying power of the cult, since the coin was minted a full 80 years after the queen’s death. According to Ariel, “It is rare to find Ptolemaic coins in Israel dating after the country came under Seleucid rule in 200 BCE. The only other gold Ptolemaic coin from an excavation in Israel (from Akko) dates from the period of Ptolemaic hegemony, in the third century BCE, and weighs less than two grams.” The excavations at Tell Kedesh, conducted since 1997, have uncovered a large Persian/ Hellenistic administrative building, complete with reception halls, dining facilities, store rooms and an archive. While the documents in the archive were not preserved, the excavations yielded 2043 bullae, from which the flourishing of the Hellenistic phase of the building can be dated to the first half of the second century BCE. Ariel notes that although the inscription on the coin identifies the queen as Arsinoë Philadelphus, “it is plausible that the second-century BCE mnaieia actually depict cryptic portraits of the reigning queens. Consequently, the queen represented on the Tell Kedesh mnaieion may actually be Cleopatra I, daughter of Antiochus III, whose marriage to Ptolemy V in 193 sealed the formal end of the Fifth Syrian War.” Some three years ago an Alexandrine hoard of Ptolemaic gold coins appeared on the world antiquities market. That hoard, however, contained no coins of Ptolemy V, so the extreme rarity of the mnaieion from Tell Kedesh remains unimpaired. Supplied by Israel Ministry of Tourism (Issue September 2010)
|

